Background
Carrier-grade NAT, also known as LSN (Large-Scale NAT), is an advanced network development to address the current bottlenecks of IPv4 and facilitates the communication between IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, and thus accelerates the transition to the latter. With the explosion of Internet consumption from mobile devices, the 32-bit address space of IPv4 is virtually insufficient to accommodate the rapidly rising demands for IP addresses. Thus, CGN has been developed to extend the use of 32-bit address space of IPv4 through address and protocol translation.
Meanwhile, the emergence of NFV (network function virtualization) architecture has virtualized all the CPEs (customer premise equipments) like routers, firewalls and even NAT (network address translation). In other words, NFV can be implemented to virtualize carrier-grade NAT onto a high-performance Intel x86 white-box server so that deployments can be simplified and flexible, while offering visibility and software-defined control f in protocol and address translation. In short, the virtualization technological concepts of NFV is the key to accelerate the transition to IPv6.
Requirements
An innovative network software vendor specialized in supplying virtualized IP routing solutions such as vADC, virtual load balancer and virtual CGNAT to service providers, operators and data centers collaborated with Lanner to jointly develop a NFV-driven networking hardware powered by x86 open architecture to address the high-availability, flexibility and scalability for virtualized NAT approach. Both parties have identified the following requirements:
High Availability
Since carrier-grade NAT is deployed to address the bottlenecks of IPv4 and is used to migrate to IPv6, the jointly developed system and its components must be able to operate continuously in an extended period of time.
2nd Gen of Scalable Xeon® Processor
The use of 2nd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors is to optimize NFV and hypervisor performances in applications with rising demands in the use of IP addresses.
Diverse Expansions via NIC Modules
To meet the networking demands in the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, the joint system shall be designed with diversified configurations for bandwidth expansions through NIC modules. The module expansion shall meet flexibility, adaptability, scalability and transformability. For instance, large CSPs shall adopt 10GbE-based appliances in their headquarter, while in remote locations, 1GbE-based hardware can operate most of the address translations.
DPDK
DPDK (Data Plane Development Kit) is a set of software libraries used to accelerate packet processing workload on Intel x86 architecture.

Solutions
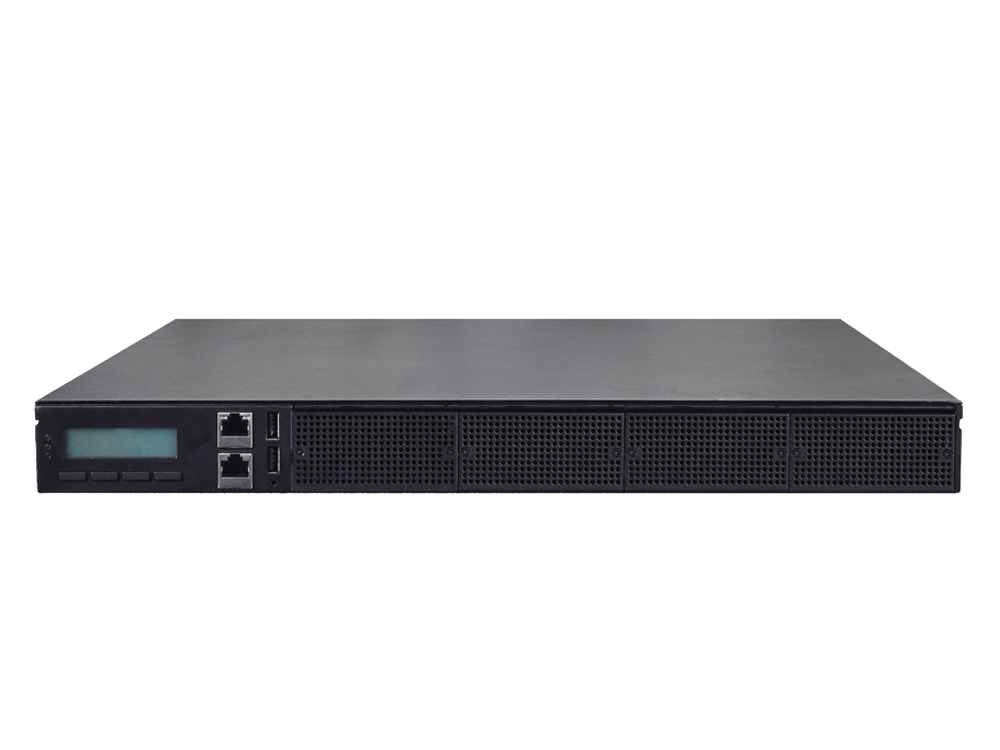
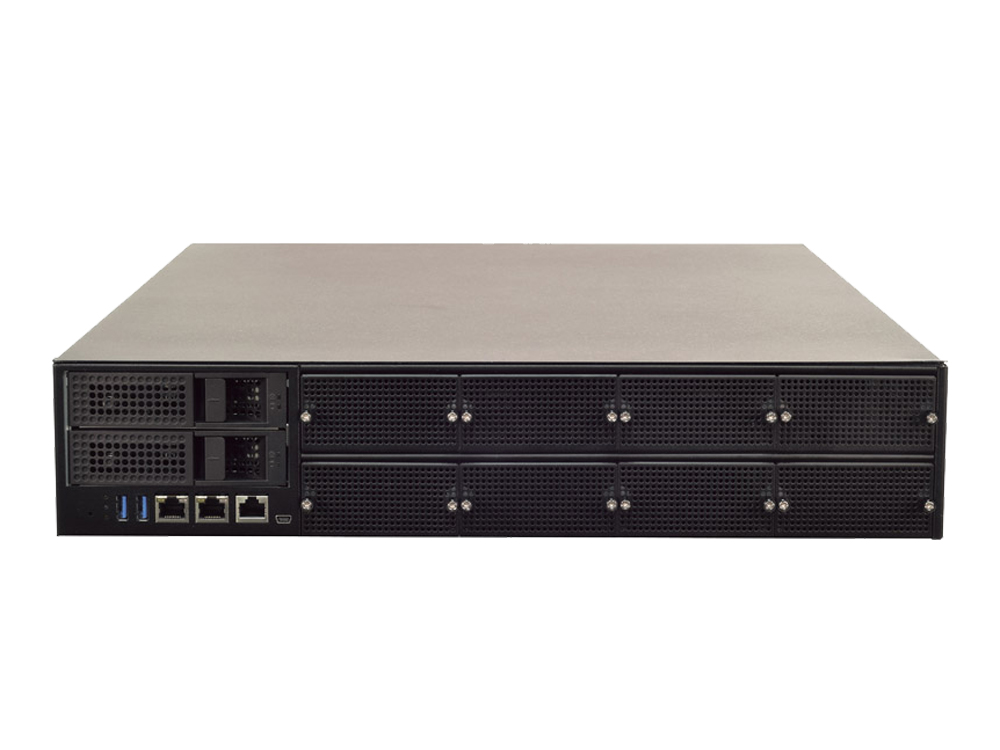
In this joint development project, Lanner presents its wide selection of network appliances powered by Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, including NCA-5510, NCA-5520, NCA-5710, and NCA-6210. For scalability and expansion, Lanner has featured its F.A.S.T (flexibility, adaptability, scalability and transformability) NIC modules with 10/25/40/100 GbE to optimize the application performance. In fact, Lanner has long-experienced skills in hardware customization to meet the actual demands.