With the advent of 5G technology, we have already seen tides of virtualization and disaggregation pushed to their peak by digitalization. Telecom vendors are forced to review their portfolios and existing solutions in order to catch up with the trends. Here comes the imminent task for the vendors – How to obtain the first-mover advantage and stand out of the competitions?
Smart Service Provider’s Choice: 5G Core Standalone NR
For service providers who are looking to deliver high-speed connectivity and boosted capacity to early adopters with 5G-enabled devices, it pretty much makes sense that, by leveraging their existing network assets and maximizing the already-installed LTE base, they can immediately promise to enable application capabilities such as AR/VR, AI, video streaming, and IoT. That’s the plan the service providers have formulated – 5G non-standalone (NSA) networks aided by 4G infrastructure before the maturation of the standalone (SA) architecture.
But for those sensible providers who have their sights set on developing futuristic network services, a completely brand-new end-to-end 5G network that no longer depends on existing LTE 4G infrastructure is the answer. Although NSA architecture serves as a temporary solution that can behave like the cloud-native SA mode, the providers will eventually have to replace it with the complex 5G core infrastructure.
If the TCO of a straight-up 5G core architecture is not higher and it seems to be merely a matter of time, why is the hesitation to embrace the ultimate 5G, Standalone NR – to unlock the full potential of the Next-G technology?
Benefits of Deploying 5G Standalone NR
Apparently, there is every reason to deploy the 5G core architecture. Any solution deployed today should offer the capabilities and flexibility customers demand now; what’s more important, it has to be future-proof. Here are some benefits that explain why 5G standalone NR deployment is the key enabler for the future development of the telecom providers:
- Facilitating the development of new use cases and devices
- Unlocking the freedom of using multiple vendors with service-based architecture
- Support for network-slicing functions that allow for advanced differentiation of network services and subscribers – a single network for everything!
- Simplified 5G RAN that contributes to the ultra-low latency and the enabling of Mobile Edge Computing (MEC)
- Assuring interoperability between network interfaces with open standard APIs– integration of systems cannot be easier!
Increased Programmability, More Possibilities – 5G VNFs as App Store
In the era of SDN and NFV, the network virtualization (or softwarization) is definitely going to pave the way for service providers’ new revenue streams in 5G service market. NFV plays an imperative part in enabling customers to optimize their network services. This process separates the hardware from the software (such as DNS and firewall) by creating a virtual network on top of the physical network, saving them from the confinement of proprietary hardware and lock-in vendor profiles – no more deficiency in interoperability with other vendor products. This decoupling of hardware and software allows service providers to expand and accelerate the development and innovation of services while improving critical network requirements such as provisioning. This technology also comes with a new potential as increasing the programmability of network applications. For service providers who are seeking various partners, they are now able to enhance and differentiate their SD-WAN offerings, gaining competitive advantages. Isn’t it Dejavu? The programmability and possibilities this technology creates are quite similar to what App Store contributed to. The use of APIs or software development kits offers third party vendors wider ranges of capabilities and more opportunities to innovate 5g service offerings, constructing the building blocks for application functions.
Back in July 2008, iPhone OS 2.0 was released along with the free software update that embedded App Store. After its debut, the subsequent success of App Store stunned Steve Jobs, who was, in the beginning, opposed to this platform because he had assumed that his team wouldn’t have this bandwidth to address the upcoming complexities. “Apple hadn’t anticipated the App Store to become this big,” said Jobs, “The mobile industry’s never seen anything like this.”
Analogously, it is foreseeable that 5G core technology will not only assist the providers and third-party vendors in the realization of programmability, but it will go further than App Store did by helping them innovate new use cases across industries through unprecedented openness of the core network.
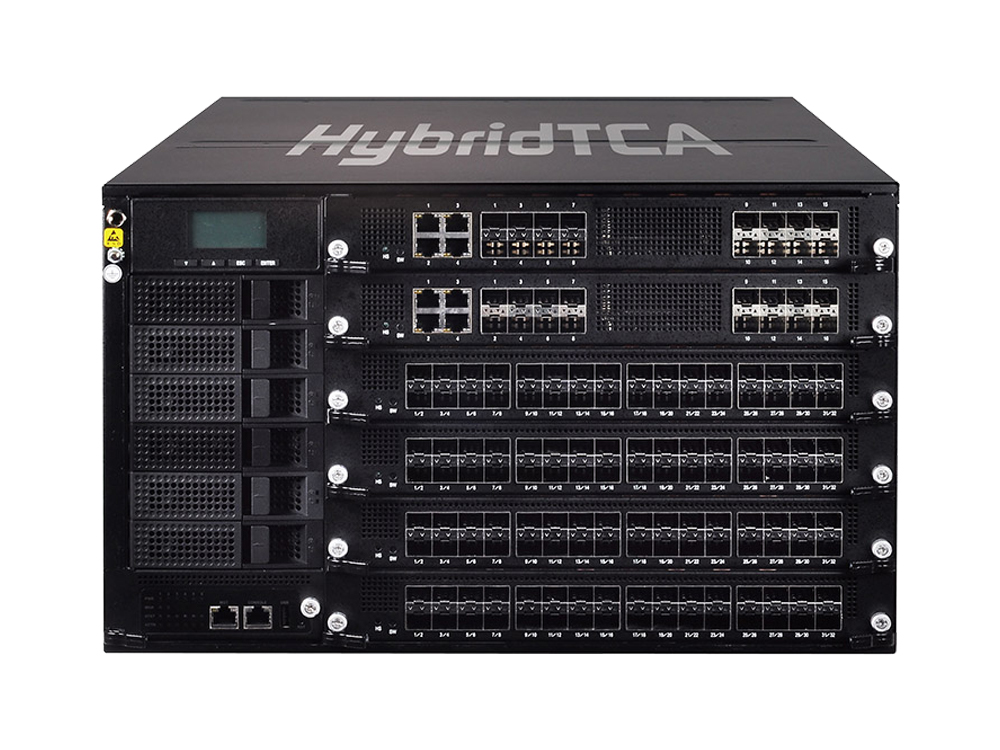
Lanner’s Offering: 5G Core-facing HTCA-6600
As 5G core technology aims to deliver capabilities that no other conventional technologies can provide, an edge computing platform that can fulfil the following demands is required:
- Ultra-low latency on data communication
- Higher security
- Network slicing
- Higher bandwidth
To satisfy the needs of the diverse industry segments and varying infrastructures, Lanner HTCA-6600 is optimized as a fully-programmable platform for edge computing applications, helping the network operators to achieve better system agility, more economical space, simplified management, flexibility and cost-saving pricing models.
The NEBS-compliant HTCA-6600 is a 6U HybridTCA 5G Core-facing NFVi-ready platform, featuring 6x CPU blades and a combination of 6x Ethernet NI/switch blade slots with full redundancy design. To ensure the carrier-grade uptime and strict reliabilities mandated by telecom networks, HTCA-6600 carries up to 6x CPU blades, each featuring dual Intel® Xeon® Processor Scalable Family CPUs and 16x DDR4 R-DIMMs, optimized for high performance in NFV applications.
To guarantee high efficiency of both controlling and allocating network resources, HTCA-6600 is equipped with 6x front-cabling, swappable Ethernet NI/switch blades, delivering a total of 32x 10GbE network ports. As the higher-end model, HTCA-6600 is designed with switch blade and CPU blade redundancy. In case one of the blades is encountered with failure, the other will take all the workloads. The cooling fans and power systems also ensure stable backup operation during system downtime.