Cloud RAN/FlexRAN: the Evolution
The increasing use of smart mobile devices has escaladed the competition among mobile operators, and the competition has driven them to upgrade bandwidth and improve quality of services, while average revenue and profitability per user are declining. This unfavorable cycle has witnessed the obstacle for the capacity of conventional RAN infrastructures as it has been challenged by the increases of volumes of data and the urged demands for high-speed communications. In fact, conventional RAN platforms are proprietary, vendor-locked deployments, and the upgrades of hardware interfaces would mean significant expenditure for mobile service operators even when profitability is declined.
The highly competitive market has driven operators to implement Cloud RAN. Cloud RAN (Radio Access Network) is anticipated as the evolution for cellular network topologies, where capacities are allocated and distributed among base stations through software means. The software-based nature of cloud RAN is thought as a cost-effective approach to replace the traditional, distributed RAN architecture to enable new serviceability and simplified deployment approach.
In the Cloud RAN approach, the architecture has evolved from analog to digital signal processing, and leverages the use of white-box hardware servers that can work flexibly with software-defined radio network functions. The white-box hardware, based on Intel x86 processor, performs general functions and signal conversions. No more proprietary ASIC or DSP is required when new generation of hardware interface is released. The Cloud RAN offers higher flexibility and saves the operating costs for cross-compatibility and hardware lifecycle.
NFV for Cloud RAN/FlexRAN
Today, Cloud RAN is also referred as Flex RAN due to the flexibility it offers to operators. Regardless of the name called, this evolved radio network architecture has become the foundation of 5G wireless network. The framework behind Cloud RAN is that, by adopting NFV (Network Function Virtualization) and cloud computing orchestrations in RAN infrastructures, operators can aggregate computing resources, service scalability, cell layers and wireless standard compatibility. Under a Cloud RAN architecture, large numbers of BBU (Baseband Unit) and RRH (Remote Radio Head) are centrally deployed as a central data center. These components are connected by cables, such as a fiber link. In other words, the components that used to be distributed are now implemented in a centralized management. Cloud RAN offers continuous economical benefits, such as simplified hardware management, software upgrades, resource pooling, lower latency and aggregated connectivity due to reduced number of sites to meet different demands for service and applications.
Virtual RAN – The Next Step
Virtual RAN, based on the hardware architecture of Cloud RAN, provides an abstraction or emulation layer, which is fully or in some degrees, connected to the hardware platform, to perform the RAN functions. Thus, the RAN architecture is virtualized for even higher flexibility.
Leveraging White-Box Hardware
No matter the Cloud RAN, FlexRAN, or Virtual RAN, the architecture no longer requires vendor-specific servers and ASIC/DSP controller interface. Instead, the evolved RAN infrastructures adopts Intel x86 white-box servers to execute applications such as MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing), network slicing, scalability and latency reduction. No more vendor-lock maintenance can save operating costs while radio functions become virtualized for easier management. At the same time, virtualized components ensure real-time performance by dynamically allocating hardware resource of the white-box server, and through centralized coordination, the performance for wireless communication services can reach macro-second level, far beyond the original millisecond stage in conventional RAN.
Summarized Advantages of FlexRAN or Cloud RAN
- Greatly reduced total cost of ownership
- No requirement for vendor-specific system
- Enables mobile edge computing and MEC
- Future-proofing RAN investment for 5G-ready platform
- Ideal for building and metro environments
Recommended Hardware
As mentioned, Cloud RAN/FlexRAN maximizes investments by adopting open platforms to act as the white-box servers to coordinate with the aggregately pooled BBUs.
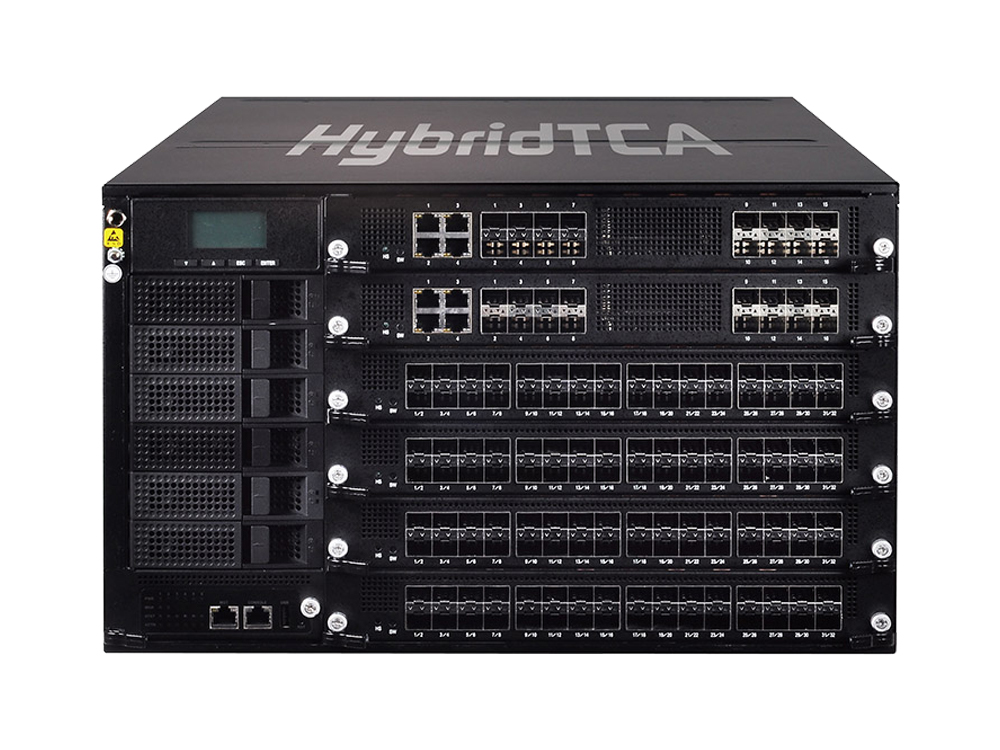
For instance, Lanner’s HTCA-6600, a 6U rackmount server featuring up to 6 CPU blades, is empowered by up to 12 dual Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600v4 processors, with a total of 264 core counts, higher memory bandwidth by DDR4 memory and Intel SR-IOV/ AVX-512 new instructions to significantly accelerate packet processing efficiency.
Regarding Cloud RAN level traffic, Lanner’s HTCA-6600 leverages the latest packet processors to offer 100GbE high-speed throughputs with capacity up to 1.2Tbps, ensured for ultra-high-performance across multiple deployment scenarios. In addition, Lanner hardware solutions are DPDK compatible for optimal efficiency.
As a Cloud RAN ready hardware, HTCA-6600 is in NEBS compliant design, full- redundancy, and carrier-grade high-availability critical to ensure 99.9999% uptimes (the six-nine). Future-proof is included in the design of the platform for future upgrades in CPU, network I/O and swappable modules.
For switch capability, HTCA-6600 is built in with BCM 56854/56860/56960 Switch Fabric.